Usage
Simply place the executable file (SorachanCoin-Core.exe) anywhere you like and run it.
After synchronization is complete, proceed to “Encrypt Wallet” from the menu.
Both consensus mechanisms “Mining (PoW)” and “Staking (PoS)” are implemented.
Address Types
- Addresses starting with “S”: ECDSA – P2PKH Transactions
Example:ScxJxQ3uD4jwWtSPmGWP3BoVjGG2PQJSqw - Addresses starting with “sora1”: Quantum-Resistant (PQC) – Schnorr Aggregated Signature SORA-QAI Transactions
Example:sora1qnr4qxnyxfpaqj6hj00vfcyv0w8tp82c6sfvr8 - Addresses starting with “cipher1”: Quantum-Resistant (PQC) – Schnorr Aggregated Signature Encrypted Communication Transactions
Example:cipher1sl2hjpvz67p9advwswtlxys0gg4xcdygpvgjt4h24wp0crvtvcwsfp2xen
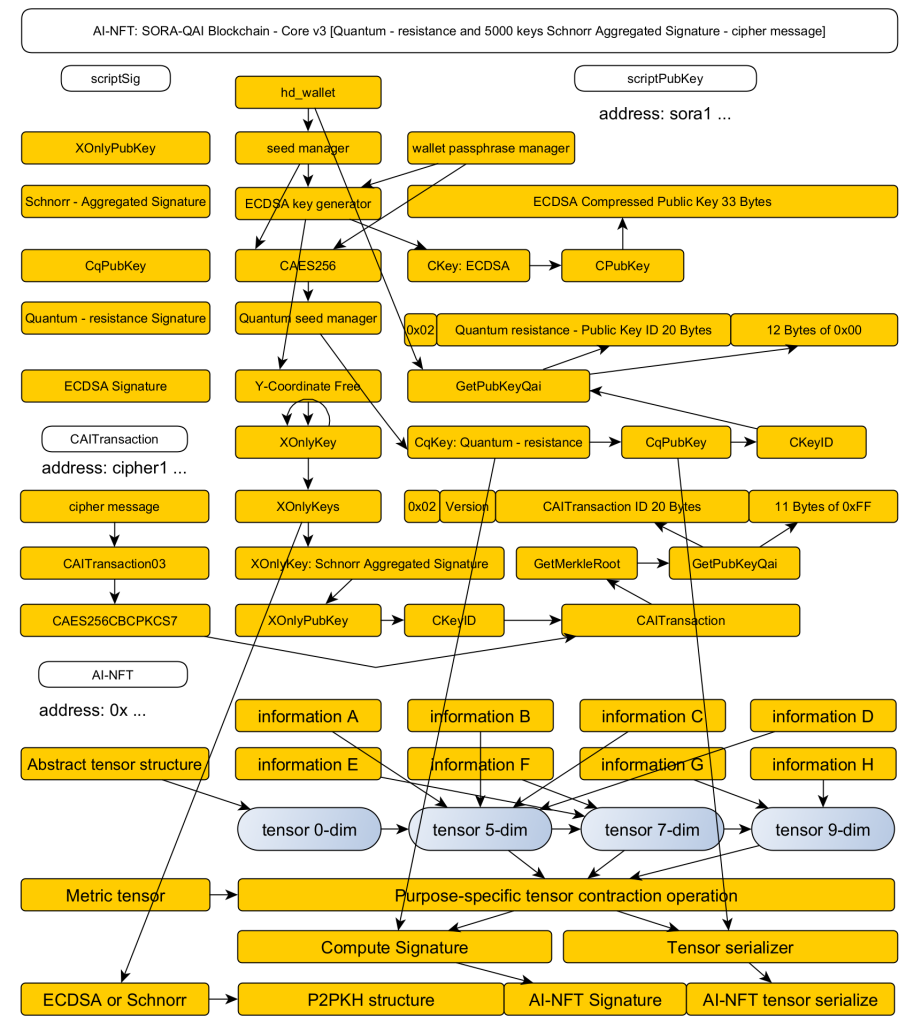
Balance Management System (Quantum-Resistant, Top Priority Design)
Available balances are calculated as the sum of:
- traditional P2PKH transactions (addresses starting with S)
- quantum-resistant Schnorr aggregated signature transactions (addresses starting with sora1)
Each is managed separately, which is the key feature of this system.
Even though balances are managed separately, compatibility is seamless:
- You can freely move funds between S → sora1 or sora1 → S without a bridge.
- Of course, transfers between S → S and sora1 → sora1 are also supported.
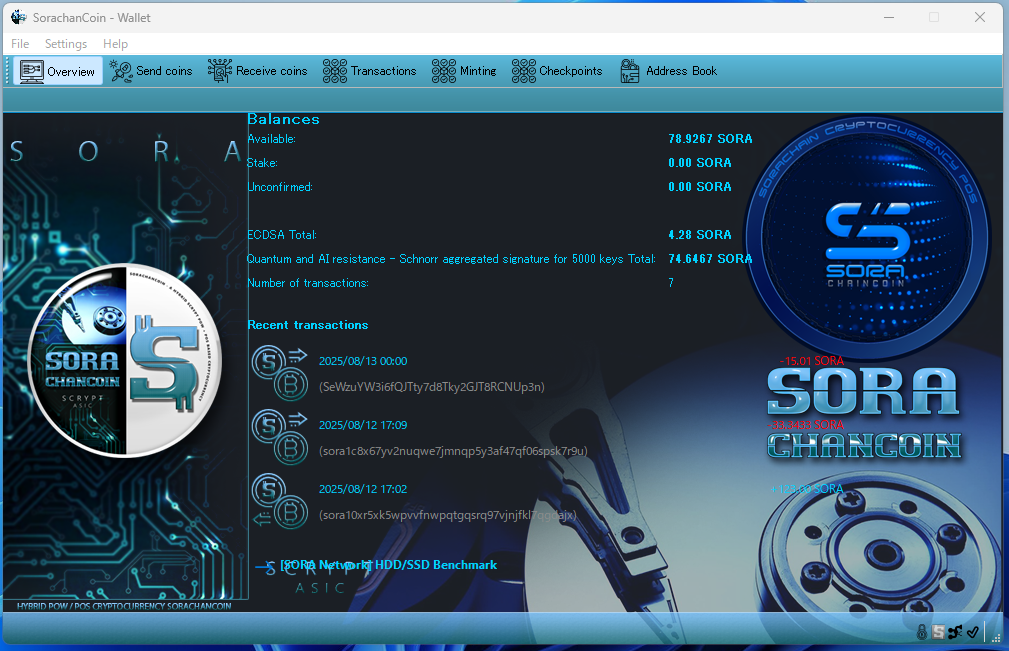
Checking Staking and Transactions
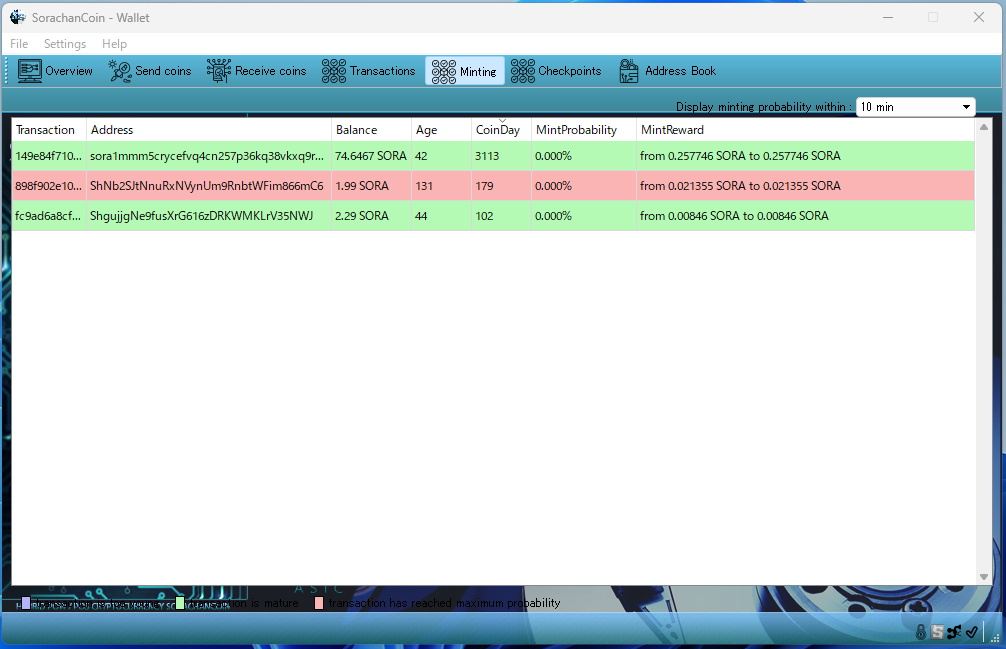
Detailed information can always be checked through each dedicated tab.
How to Use Each Address
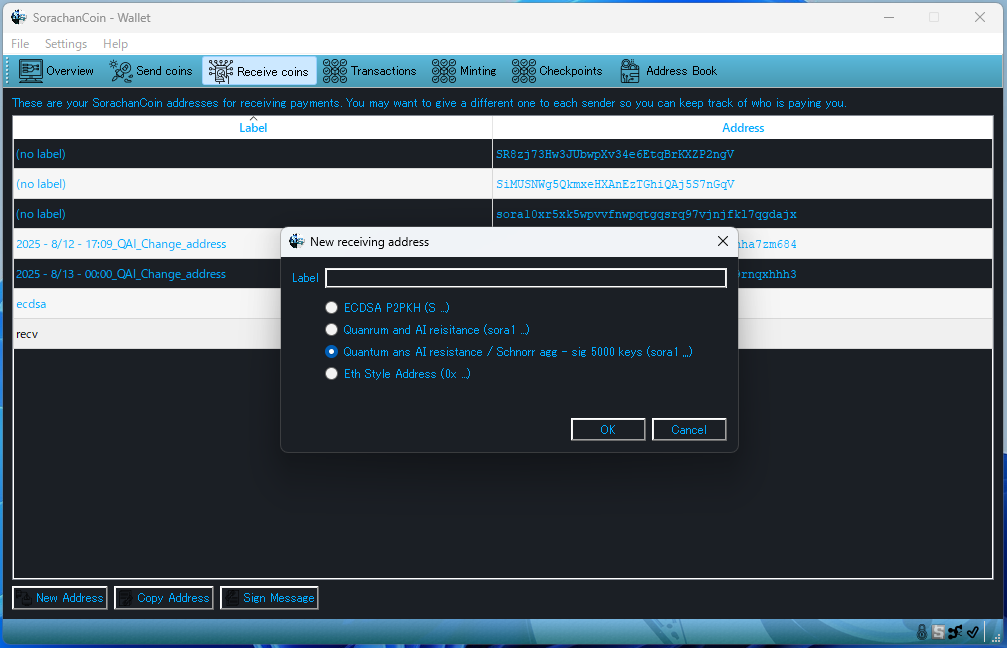
When generating a new address (e.g., for receiving SORA), you will choose from four types:
(There are two sora1 options because you can select whether to use Schnorr aggregated signature multisig (5000-key). Both are fully supported.)
- ECDSA Address (S …)
- Quantum AI-Resistant Address (sora1 …)
- Quantum AI-Resistant + Schnorr Aggregated Signature (5000 keys) Address (sora1 …)
- Ethereum-Style Address (0x …)
Encrypted Communication Feature
The debug window in the menu now includes an encrypted communication function.
- Keys are exchanged via the blockchain, and encrypted communication is then established based on that information.
- SORA-QAI Anonymous Encrypted Communication Message Addresses begin with cipher1.
On this screen, you can view a list of all messages sent to you.
When a message is sent to a cipher1 address, it is transmitted via the blockchain and securely exchanged in encrypted form.
Decentralized Security
This system operates without a central server, running instead on a decentralized blockchain.
Thus, there is no risk of interception by relay servers along the communication path.
In a typical centralized server system, SSL encrypts the communication path, but messages are decrypted inside the server for processing—creating a structural flaw, as administrators can see the data.
In contrast, this system has no central node performing decryption, meaning the risk of message leakage to third parties is virtually eliminated.
It achieves safe, private communication unique to decentralized systems.